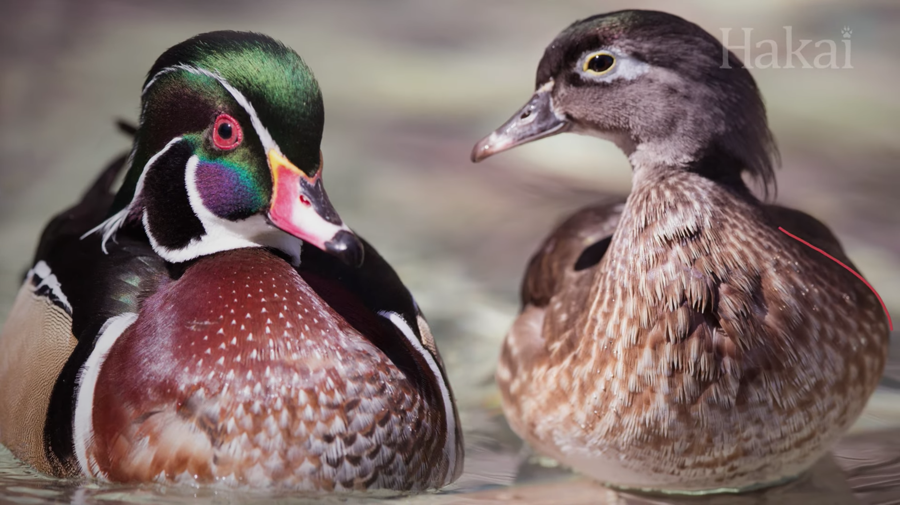
“If you’re new to birdwatching, you might start to wonder why are male birds so often vibrant while the females are kind of dull. Sexual dimorphism is the difference in size, shape, or color between the sexes of a single species.”
As this Hakai Institute video explains, you can spot sexual dimorphism throughout the animal kingdom, not only in bird examples like harlequin ducks and peafowl.
“To simplify things, we’re talking in binaries male and female. But in reality, the nature of biological sex is much richer and more complex.”


Lions, orangutans, elephant seals, deer, kangaroos, seahorses, mandrills, the Triplewart seadevil, and many other animals have generally evolved to look or act differently to help compete for mates, to provide different types of parental care, to camouflage into their environments, and more.
This video is an episode of Long Story Shorts, quick coastal science explainers by the team at the Hakai Institute.
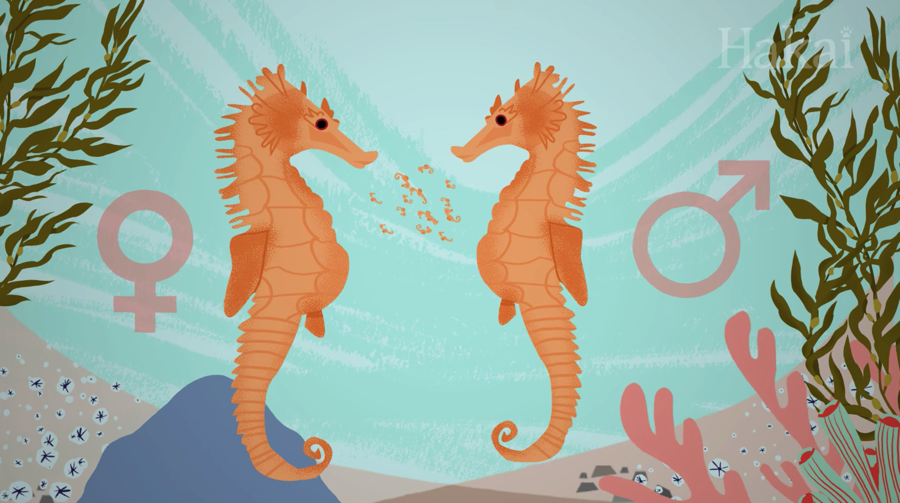

Watch more from Hakai.org on YouTube or Instagram.
And find Hakai videos on TKSST. Watch these videos next:
• The male rock greenling’s ‘psychedelic rainbow coloration’
• What to Expect From an Expecting Seahorse
• The Peacock Spiders of Australia
• The Cornell Lab of Ornithology‘s Birds of Paradise project
• How did feathers evolve? The connections between dinosaurs and birds
Curated, kid-friendly, independently-published. Support this mission by becoming a sustaining member today.

